Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
If M = 3,000, P = 2, and Y = 12,000, what is
velocity?
|
|
|
2.
|
When the price level rises, the number of dollars needed to buy a representative
basket of goods
a. | increases, and so the value of money rises. | b. | increases, and so
the value of money falls. | c. | decreases, and so the value of money
rises. | d. | decreases, and so the value of money falls |
|
|
|
3.
|
When the money market is drawn with the value of money on the vertical axis, as
the price level increases, the value of money
a. | increases, so the quantity of money demanded increases. | b. | increases, so the
quantity of money demanded decreases. | c. | decreases, so the quantity of money demanded
decreases. | d. | decreases, so the quantity of money demanded
increases. |
|
|
|
4.
|
The price level falls. This might be because the Federal Reserve
a. | bought bonds which raised the money supply. | b. | bought bonds which
reduced the money supply. | c. | sold bonds which raised the money
supply. | d. | sold bonds which reduced the money supply. |
|
|
|
Figure 1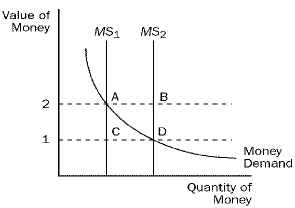
|
|
|
5.
|
Refer to Figure 1. If the current money supply is MS1,
then
a. | there is no excess supply or excess demand if the value of money is
2. | b. | the equilibrium is at point C. | c. | there is an excess supply of money if the value
of money is 1. | d. | None of the above is correct. |
|
|
|
6.
|
Economic variables whose values are measured in goods are called
a. | dichotomous variables. | b. | nominal variables. | c. | classical
variables. | d. | real variables. |
|
|
|
7.
|
Velocity is computed as
a. | (P 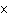 Y)/M. Y)/M. | b. | (P 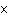 M)/Y.
M)/Y. | c. | (Y 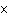 M)/P.
M)/P. | d. | (Y 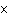 M)/V.
M)/V. |
|
|
|
8.
|
According to the assumptions of the quantity theory of money, if the money
supply increases by 5 percent, then
a. | nominal and real GDP would rise by 5 percent. | b. | nominal GDP would
rise by 5 percent; real GDP would be unchanged. | c. | nominal GDP would be unchanged; real GDP would
rise by 5 percent. | d. | neither nominal GDP nor real GDP would
change. |
|
|
|
9.
|
Based on past experience, if a country is experiencing hyperinflation, then
which of the following would be a reasonable guess?
a. | The country has high money supply growth. | b. | Inflation is acting
like a tax on everyone who holds money. | c. | The government is printing money to finance its
expenditures. | d. | All of the above are correct. |
|
|
|
10.
|
Printing money to finance government expenditures
a. | causes the value of money to rise. | b. | imposes a tax on everyone who holds
money. | c. | is the principal method by which the U.S. government finances its
expenditures. | d. | None of the above is correct. |
|
|
|
11.
|
The Fisher effect says that
a. | the nominal interest rate adjusts one for one with the inflation
rate. | b. | the growth rate of the money supply is negatively related to the velocity of
money. | c. | real variables are heavily influenced by the monetary system. | d. | All of the above are
correct. |
|
|
|
12.
|
The shoeleather cost of inflation refers to
a. | the redistributional effects of unexpected inflation. | b. | the time spent
searching for low prices when inflation rises. | c. | the waste of resources used to maintain lower
money holdings. | d. | the increased cost to the government of printing more
money. |
|
|
|
13.
|
The costs of changing price tags and price listings are known as
a. | inflation-induced tax distortions. | b. | relative-price variability
costs. | c. | shoeleather costs. | d. | menu costs. |
|
|
|
14.
|
Wealth is redistributed from creditors to debtors when inflation was expected to
be
a. | high and it turns out to be high. | b. | low and it turns out to be
low. | c. | low and it turns out to be high. | d. | high and it turns out to be
low. |
|
|
|
15.
|
Net exports of a country are the value of
a. | goods and services imported minus the value of goods and services
exported. | b. | goods and services exported minus the value of goods and services
imported. | c. | goods exported minus the value of goods imported. | d. | goods imported minus
the value of goods exported. |
|
|
|
16.
|
Which of the following both raise net exports?
a. | exports rise, imports rise | b. | exports rise, imports fall | c. | imports rise,
exports rise | d. | imports rise, exports fall |
|
|
|
17.
|
Net capital outflow measures
a. | foreign assets held by domestic residents minus domestic assets held by foreign
residents. | b. | the imbalance between the amount of foreign assets bought by domestic residents and
the amount of domestic assets bought by foreigners. | c. | the imbalance between the amount of foreign
assets bought by domestic residents and the amount of domestic goods and services sold to
foreigners. | d. | None of the above is correct. |
|
|
|
18.
|
When Microsoft establishes a distribution center in France, U.S. net capital
outflow
a. | increases because Microsoft makes a portfolio investment in
France. | b. | decreases because Microsoft makes a portfolio investment in
France. | c. | increases because Microsoft makes a direct investment in capital in
France. | d. | decreases because Microsoft makes a direct investment in capital
France. |
|
|
|
19.
|
Which of the following is always correct?
a. | Y - I = NCO | b. | NCO = NX | c. | NX =
I | d. | All of the above are correct. |
|
|
|
20.
|
A U.S. firm exchanges dollars for yen and then uses them to buy Japanese
goods. Overall as a result of these transactions
a. | both U.S. net capital outflow and U.S. net exports rise. | b. | both U.S. net
capital outflow and U.S. net exports fall. | c. | U.S. net capital outflow rises and U.S. net
exports fall. | d. | U.S. net capital outflow falls and U.S. net exports
rise. |
|
|
|
21.
|
If a country has business opportunities that are relatively attractive to other
countries, we would expect it to have
a. | both positive net exports and positive net capital outflow. | b. | both negative net
exports and negative net capital outflow. | c. | positive net exports and negative net capital
outflow. | d. | negative net exports and positive net capital
outflow. |
|
|
|
22.
|
A country has $45 million of domestic investment and net capital outflow of -$60
million. What is its saving?
a. | $15 million. | b. | -$15 million. | c. | $105
million. | d. | -$105 million. |
|
|
|
23.
|
The country of Sylvania has a GDP of $900, investment of $200, government
purchases of $200, and net capital outflow of -$100. What is consumption?
|
|
|
24.
|
If the exchange rate were .8 Canadian dollars per U.S. dollar, a watch that
costs $8 US dollars would cost
a. | 6.4 Canadian dollars. | b. | 10 Canadian dollars. | c. | 12.50 Canadian
dollars. | d. | None of the above is correct. |
|
|
|
25.
|
When a country's central bank increases the money supply, a unit of
money
a. | gains value both in terms of the domestic goods and services it can buy and in terms
of the foreign currency it can buy. | b. | gains value in terms of the domestic goods and
services it can buy, but loses value in terms of the foreign currency it can buy. | c. | loses value in terms
of the domestic goods and services it can buy, but gains value in terms of the foreign currency it
can buy. | d. | loses value both in terms of the domestic goods and services it can buy and in terms
of the foreign currency it can buy. |
|
|
|
26.
|
According to purchasing-power parity, if prices in the United States increase by
a smaller percentage than prices in Poland, then
a. | the real exchange defined as Polish goods per unit of U.S. goods
rises. | b. | the real exchange defined as Polish goods per unit of U.S. goods
falls. | c. | the nominal exchange rate defined as Polish currency per dollar
rises. | d. | the nominal exchange rate defined as Polish currency per dollar
falls. |
|
|
|
27.
|
Purchasing-power parity theory does not hold at all times because
a. | many goods are not easily transported. | b. | the same goods produced in different countries
may be imperfect substitutes for each other. | c. | Both a and b are correct. | d. | prices are different
across countries. |
|
|
|
28.
|
Over the past two decades, the United States has
a. | generally had, or been very near to a trade balance. | b. | had trade deficits
in about as many years as it has trade surpluses. | c. | persistently had a trade
deficit. | d. | persistently had a trade surplus. |
|
|
|
29.
|
In the open-economy macroeconomic model, the supply of loanable funds comes
from
a. | national saving. | b. | private saving. | c. | domestic
investment. | d. | the sum of domestic investment and net capital
outflow. |
|
|
|
30.
|
In an open economy, the demand for loanable funds comes from
a. | only those who want to borrow funds to buy domestic capital
goods. | b. | only those who want to borrow funds to buy foreign assets. | c. | those who want to
borrow funds to buy either domestic capital goods or foreign assets. | d. | neither those who
want to borrow funds to buy domestic capital goods nor those who want to borrow funds to buy foreign
assets. |
|
|
|
31.
|
In the open-economy macroeconomic model, the supply of loanable funds
equals
a. | national saving. The demand for loanable funds comes from domestic investment + net
capital outflow. | b. | national saving. The demand for loanable funds comes only from domestic
investment. | c. | private saving. The demand for loanable funds comes from domestic investment + net
capital outflow. | d. | private saving. The demand for loanable funds comes only from domestic
investment. |
|
|
|
32.
|
If the demand for loanable funds shifts right, then
a. | the real interest rate and the equilibrium quantity of loanable funds both
fall. | b. | the real interest rate falls and the equilibrium quantity of loanable funds
rises. | c. | the real interest rate and the equilibrium quantity of loanable funds both
rise. | d. | the real interest rate rises and the equilibrium quantify of loanable funds
falls. |
|
|
|
33.
|
In an open economy,
a. | net capital outflow = imports. | b. | net capital outflow = net
exports. | c. | net capital outflow = exports. | d. | None of the above is
correct. |
|
|
|
34.
|
In the open economy macroeconomic model, the amount of dollars demanded in the
market for foreign-currency exchange at a given real exchange rate increases if
a. | either U.S. imports or exports increase. | b. | either U.S. imports
or exports decrease. | c. | either U.S. imports increase or U.S. exports
decrease. | d. | either U.S. imports decrease or U.S. exports
increase. |
|
|
|
35.
|
The variable that links the market for loanable funds and the market for
foreign-currency exchange is
a. | net capital outflow. | b. | national saving. | c. | exports. | d. | domestic
investment. |
|
|
|
36.
|
U.S. net capital outflow
a. | is a source of the supply of loanable funds, and the source of the supply of dollars
in the foreign exchange market. | b. | is a source of the supply of loanable funds,
and a source of the demand for dollars in the foreign exchange market. | c. | is a part of the
demand for loanable funds, and the source of the supply of dollars in the foreign exchange
market. | d. | is a part of the demand for loanable funds, and a source of the demand for dollars in
the foreign exchange market. |
|
|
|
Figure 2
Refer to this diagram to answer the questions
below.
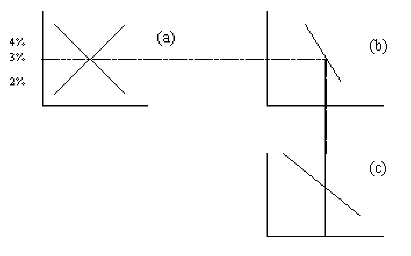
|
|
|
37.
|
Refer to Figure 2. The curve in panel b shows that as the interest rate
rises,
a. | domestic investment declines. | b. | net capital outflow
declines. | c. | net capital outflow and domestic investment decline. | d. | None of the above is
correct. |
|
|
|
38.
|
Refer to Figure 3. Which curve shows the relation between the exchange
rate and net exports?
a. | the demand curve in panel a. | b. | the demand curve in panel
c. | c. | the supply curve in panel a. | d. | the supply curve in panel
c. |
|
|
|
39.
|
A government budget deficit
a. | increases both net capital outflow and net exports. | b. | decreases both net
capital outflow and net exports. | c. | increases net capital outflow and decreases net
exports. | d. | decreases net capital outflow and increases net
exports. |
|
|
|
40.
|
Trade policies
a. | alter the trade balance because they alter imports of the country that implemented
them. | b. | alter the trade balance because they alter net capital outflow of the country that
implemented them. | c. | do not alter the trade balance because they
cannot alter the national saving or domestic investment of the country that implements
them. | d. | do not alter the trade balance because they cannot alter the real exchange rate of
the currency of the country that implements them. |
|