Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
Which of the following is not a determinant of the price elasticity of
demand for a good?
a. | the time horizon | b. | the steepness or flatness of the supply curve
for the good | c. | the definition of the market for the good | d. | the availability of
substitutes for the good |
|
|
|
2.
|
If the price elasticity of demand is 1.5, regardless of which two points on the
demand curve are used to compute the elasticity, then
a. | demand is perfectly inelastic, and the demand curve is vertical. | b. | demand is elastic,
and the demand curve is a straight, downward-sloping line. | c. | demand is perfectly
elastic, and the demand curve is horizontal. | d. | demand is elastic, and the demand curve is
something other than a straight, downward-sloping line. |
|
|
|
Figure 1
|
|
|
3.
|
Refer to Figure 1. The section of the demand curve from B to C represents
the
a. | elastic section of the demand curve. | b. | perfectly elastic section of the demand
curve. | c. | unit elastic section of the demand curve. | d. | inelastic section of
the demand curve. |
|
|
|
4.
|
Refer to Figure 1. If the price decreases in the region of the demand
curve between points A and B, we can expect total revenue to
a. | increase. | b. | stay the same. | c. | decrease. | d. | first decrease, then increase until total
revenue is maximized. |
|
|
|
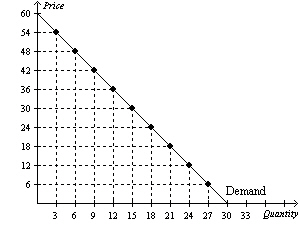
Figure 2
|
|
|
5.
|
Refer to Figure 2. Using the midpoint method, between prices of $12 and
$18, price elasticity of demand is
a. | 0.33. | b. | 0.67. | c. | 1.33. | d. | 1.89. |
|
|
|
6.
|
Suppose demand is perfectly elastic, and the supply of the good in question
decreases. As a result,
a. | the equilibrium quantity decreases, and the equilibrium price is
unchanged. | b. | the equilibrium price increases, and the equilibrium quantity is
unchanged. | c. | the equilibrium quantity and the equilibrium price both are
unchanged. | d. | buyers’ total expenditure on the good is
unchanged. |
|
|
|
7.
|
A perfectly inelastic demand implies that buyers
a. | decrease their purchases when the price rises. | b. | purchase the same
amount as before when the price rises or falls. | c. | increase their purchases only slightly when the
price falls. | d. | respond substantially to an increase in price. |
|
|
|
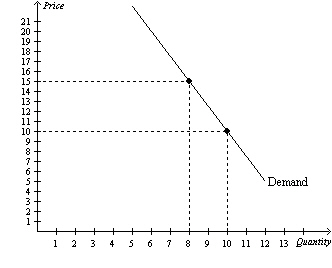
Figure 3
|
|
|
8.
|
Refer to Figure 3. A decrease in price from $15 to $10 leads to
a. | a decrease in total revenue of $10, so the price elasticity of demand is greater than
1 in this price range. | b. | a decrease in total revenue of $10, so the
price elasticity of demand is less than 1 in this price range. | c. | a decrease in total
revenue of $20, so the price elasticity of demand is less than 1 in this price
range. | d. | a decrease in total revenue of $20, so demand is elastic in this price
range. |
|
|
|
9.
|
You are in charge of the local city-owned golf course. You need to increase the
revenue generated by the golf course in order to meet expenses. The mayor advises you to increase the
price of a round of golf. The city manager recommends reducing the price of a round of golf. You
realize that
a. | the mayor thinks demand is elastic, and the city manager thinks demand is
inelastic. | b. | both the mayor and the city manager think that demand is elastic. | c. | both the mayor and
the city manager think that demand is inelastic. | d. | the mayor thinks demand is inelastic, and the
city manager thinks demand is elastic. |
|
|
|
10.
|
Eric produces jewelry boxes. If the demand for jewelry boxes is elastic and Eric
wants to increase his total revenue, he should
a. | increase the price of his jewelry boxes. | b. | decrease the price
of his jewelry boxes. | c. | not change the price of his jewelry
boxes. | d. | None of the above answers is correct. |
|
|
|
11.
|
The price elasticity of supply measures how responsive
a. | sellers are to a change in price. | b. | sellers are to a change in buyers'
income. | c. | buyers are to a change in production costs. | d. | equilibrium price is
to a change in supply. |
|
|
|
12.
|
When a supply curve is relatively flat,
a. | sellers are not at all responsive to a change in price. | b. | the equilibrium
price changes substantially when the demand for the good changes. | c. | the supply is
relatively elastic. | d. | the supply is relatively
inelastic. |
|
|
|
Figure 4The following figure shows the supply curve for a
particular good. 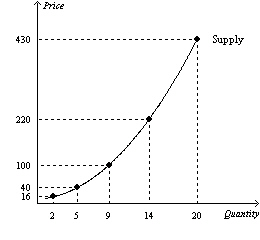
|
|
|
13.
|
Refer to Figure 4. Using the midpoint method, what is the price
elasticity of supply between $100 and $220?
|
|
|
14.
|
If a nonbinding price ceiling is imposed on a market, then
a. | the quantity sold in the market will decrease. | b. | the quantity sold in
the market will stay the same. | c. | the price in the market will
increase. | d. | the price in the market will decrease. |
|
|
|
15.
|
If a binding price ceiling is imposed on the computer market, then
a. | the quantity of computers demanded will increase. | b. | the quantity of
computers supplied will decrease. | c. | a shortage of computers will
develop. | d. | All of the above are correct. |
|
|
|
16.
|
In the housing market, rent control causes
a. | quantity supplied and quantity demanded to fall. | b. | quantity supplied to
fall and quantity demanded to rise. | c. | quantity supplied to rise and quantity demanded
to fall. | d. | quantity supplied and quantity demanded to rise. |
|
|
|
17.
|
Suppose the government has imposed a price floor on televisions. Which of
the following events could transform the price floor from one that is not binding into one that is
binding?
a. | Firms expect the price of televisions to rise in the future. | b. | The number of firms
selling televisions decreases. | c. | Consumers' income decreases, and
televisions are a normal good. | d. | The number of consumers buying televisions
increases. |
|
|
|
18.
|
If the minimum wage exceeds the equilibrium wage, then
a. | the quantity demanded of labor will exceed the quantity supplied. | b. | the quantity
supplied of labor will exceed the quantity demanded. | c. | the minimum wage will not be
binding. | d. | there will be no unemployment. |
|
|
|
Table 1Price | Quantity
Demanded | Quantity
Supplied | $0 | 12 | 0 | $1 | 10 | 2 | $2 | 8 | 4 | $3 | 6 | 6 | $4 | 4 | 8 | $5 | 2 | 10 | $6 | 0 | 12 | | | |
|
|
|
19.
|
Refer to Table 1. Suppose the government imposes a price ceiling of
$1 on this market. What will be the size of the shortage in this market?
a. | 0 units | b. | 2 units | c. | 8
units | d. | 10 units |
|
|
|
Table 2Price | Quantity
Demanded | Quantity
Supplied | $0 | 250 | 0 | $5 | 200 | 75 | $10 | 150 | 150 | $15 | 100 | 225 | $20 | 50 | 300 | $25 | 0 | 375 | | | |
|
|
|
20.
|
Refer to Table 2. Which of the following statements is
correct?
a. | A price ceiling set at $15 will be binding and will result in a shortage of 50
units. | b. | A price ceiling set at $15 will be binding and will result in a shortage of 100
units. | c. | A price ceiling set at $15 will be binding and will result in a shortage of 125
units. | d. | A price ceiling set at $15 will not be binding. |
|
|
|
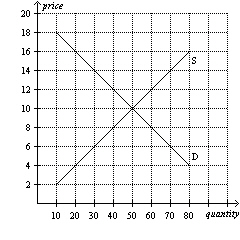
Figure 5
|
|
|
21.
|
Refer to Figure 5. Which of the following price floors would be
binding in this market?
|
|
|
22.
|
Refer to Figure 5. If the government imposes a price ceiling of $8
on this market, then there will be a
a. | shortage of 0. | b. | shortage of 10. | c. | shortage of
20. | d. | shortage of 40. |
|
|
|
23.
|
If a tax is levied on the buyers of a product, then the supply curve
a. | will not shift. | b. | will shift up. | c. | will shift
down. | d. | will become flatter. |
|
|
|
24.
|
When a tax is imposed on the buyers of a good, the demand curve shifts
a. | upward by the amount of the tax. | b. | downward by the amount of the
tax. | c. | upward by less than the amount of the tax. | d. | downward by less
than the amount of the tax. |
|
|
|
25.
|
A tax on the buyers of popcorn
a. | increases the size of the popcorn market. | b. | decreases the size
of the popcorn market. | c. | has no effect on the size of the popcorn
market. | d. | may increase, decrease, or have no effect on the size of the popcorn
market. |
|
|
|
26.
|
The price paid by buyers in a market will decrease if the government
a. | increases a binding price floor in that market. | b. | increases a binding
price ceiling in that market. | c. | decreases a tax on the good sold in that
market. | d. | More than one of the above is correct. |
|
|
|
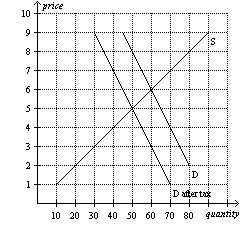
Figure 6
|
|
|
27.
|
Refer to Figure 6. The equilibrium price in the market before the
tax is imposed is
|
|
|
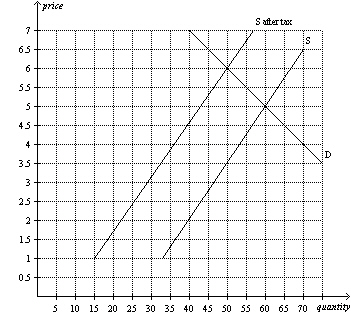
Figure 7
|
|
|
28.
|
Refer to Figure 7. The amount of the tax per unit is
a. | $1. | b. | $1.50. | c. | $2.50. | d. | $3.50. |
|
|
|
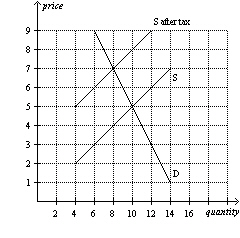
Figure 8
|
|
|
29.
|
Refer to Figure 8. The price paid by buyers after the tax is
imposed is
|
|
|
30.
|
Suppose that a tax is placed on books. If the sellers pay the majority of
the tax, then we know that the
a. | demand is more inelastic than the supply. | b. | supply is more
inelastic than the demand. | c. | government has required that buyers remit the
tax payments. | d. | government has required that sellers remit the tax
payments. |
|
|
|
Figure 6-16
Panel (a) | Panel (b) | | | | 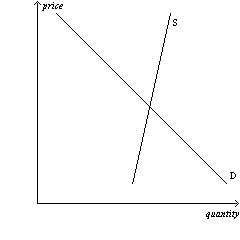 | 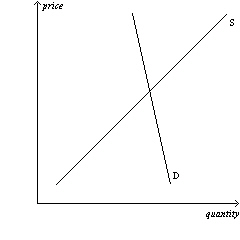 | Panel (c) | 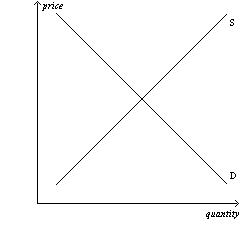 | | | | |
|
|
|
31.
|
Refer to Figure 6-16. In which market will the majority of the tax
burden fall on sellers?
a. | market (a) | b. | market (b) | c. | market
(c) | d. | All of the above are correct. |
|
|
|
32.
|
On a graph, the area below a demand curve and above the price measures
a. | producer surplus. | b. | consumer surplus. | c. | deadweight
loss. | d. | willingness to pay. |
|
|
|
33.
|
Suppose Katie, Kendra, and Kristen each purchase a particular type of cell phone
at a price of $80. Katie’s willingness to pay was $100, Kendra’s willingness to pay was
$95, and Kristen's willingness to pay was $80. Which of the following statements is
correct?
a. | For the three individuals together, consumer surplus amounts to
$35. | b. | Having bought the cell phone, Kristen is better off than she would have been had she
not bought it. | c. | Had the price of the cell phone been $95 rather than $80, Katie and Kendra definitely
would have been buyers and Kristen definitely would not have been a buyer. | d. | The fact that all
three individuals paid $80 for the same type of cell phone indicates that each one placed the same
value on that cell phone. |
|
|
|
34.
|
Carla would be willing to pay $500 to see Shakira, but she buys a ticket for
$200. Calra values the performance at
a. | $200. | b. | $300. | c. | $500. | d. | $800. |
|